Synchronize Time using GPS
1 Overview
Hesai lidar products support the use of the GNSS_NMEA protocol (GPRMC or GPGGA) to achieve precise time synchronization between the lidar and the system by relying on an external clock source to obtain absolute time.
- GPS: Global Positioning System, developed and operated by the U.S. government, is a satellite navigation system.
- GNSS: Global Navigation Satellite System, refers to all satellite systems capable of providing global or regional positioning, navigation and timing services, including GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, GALILEO, etc.
Note: In this document, the terms GPS and GNSS are used interchangeably and do not specifically refer to the U.S. GPS system.
2 Application Method
To synchronize GNSS time on the lidar, it needs to be connected to a third-party GNSS module to obtain PPS signals and NMEA information. The specific methods and steps are as follows:
Note: This document uses Pandar128 and JT16 as examples. JT16 only supports GPS time synchronization.
2.1 Hardware Connection
2.1.1 Pandar128
- Pin definitions on the lidar side:
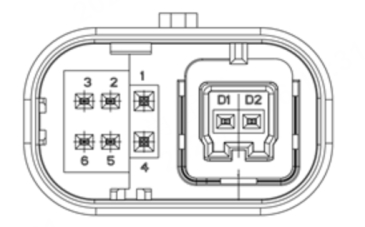
- Pin definitions on the connection box side (if used):
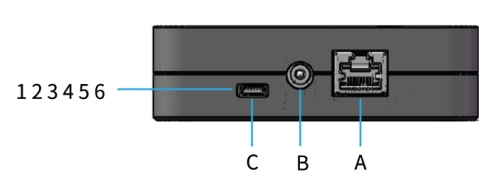
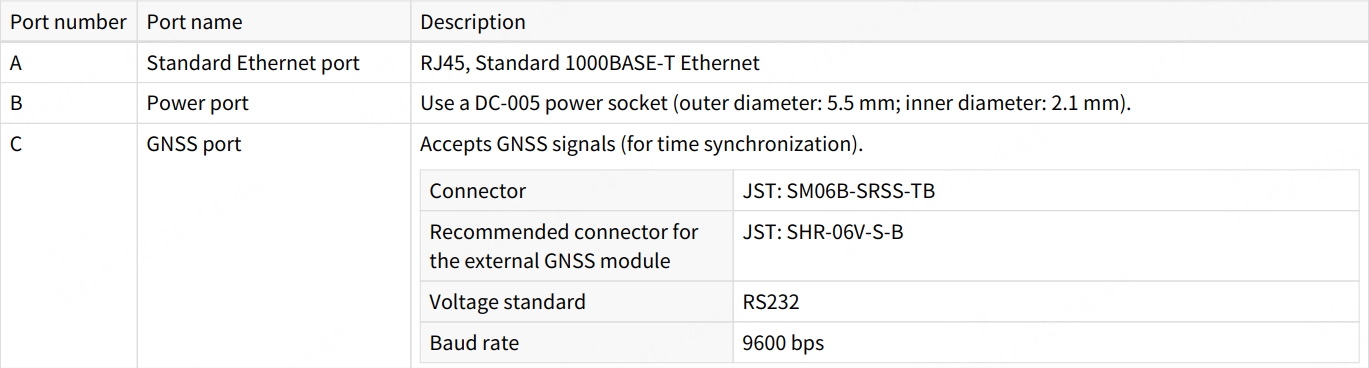
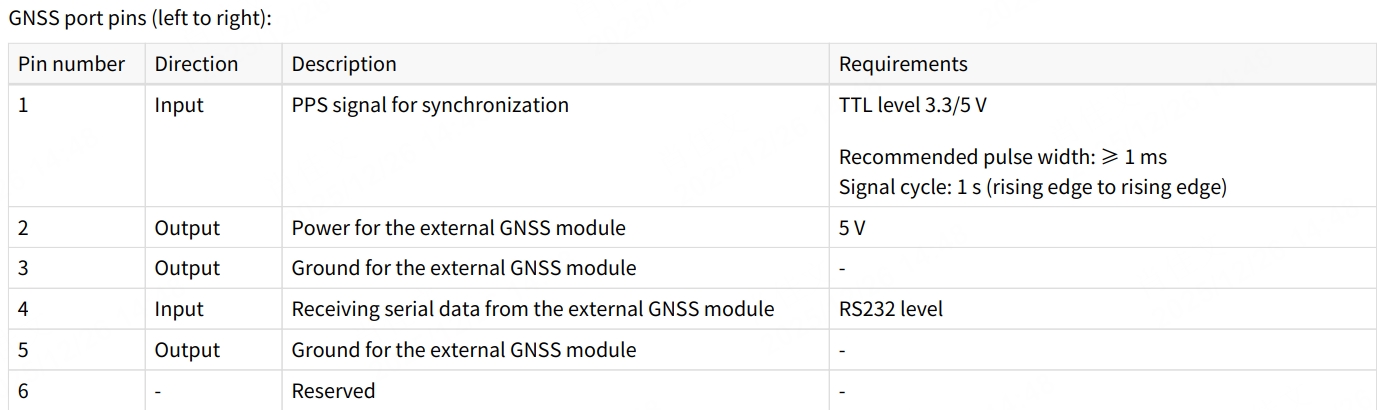
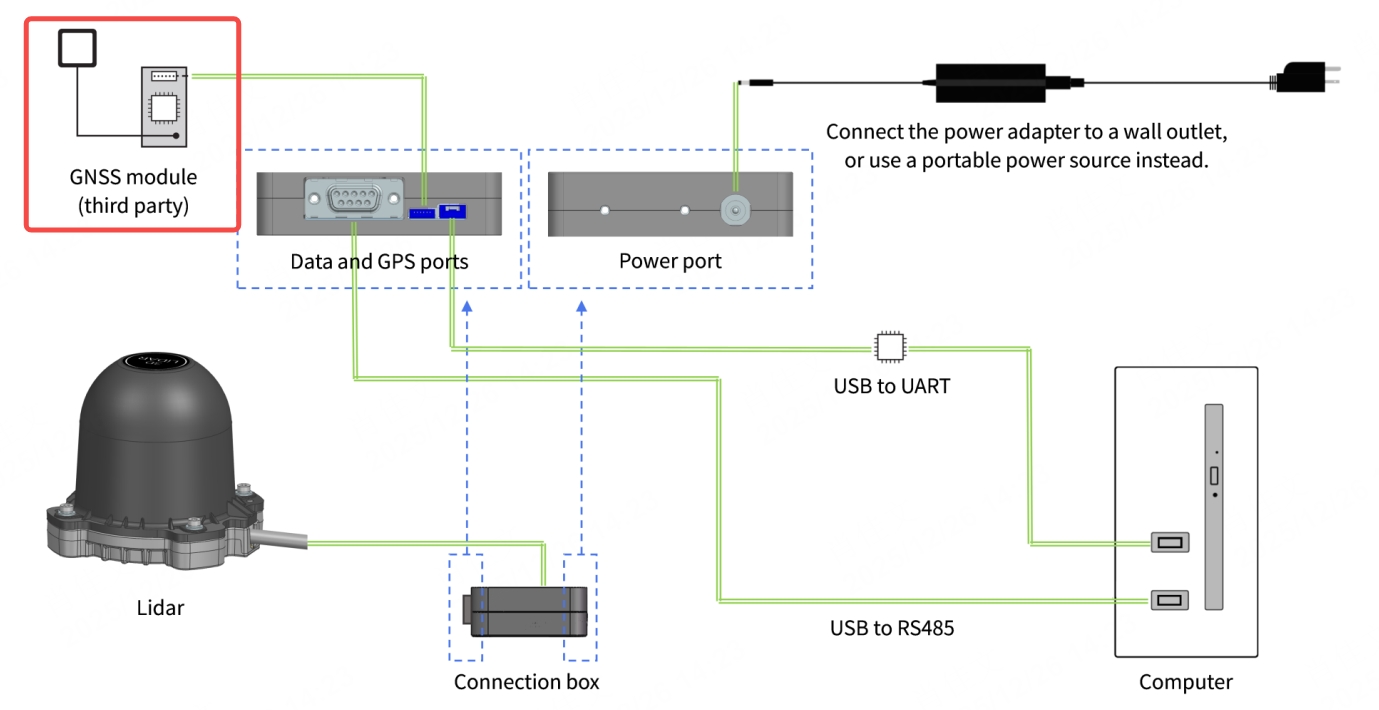
- If the connection box is connected to the GNSS module, refer to the hardware connection diagram below:
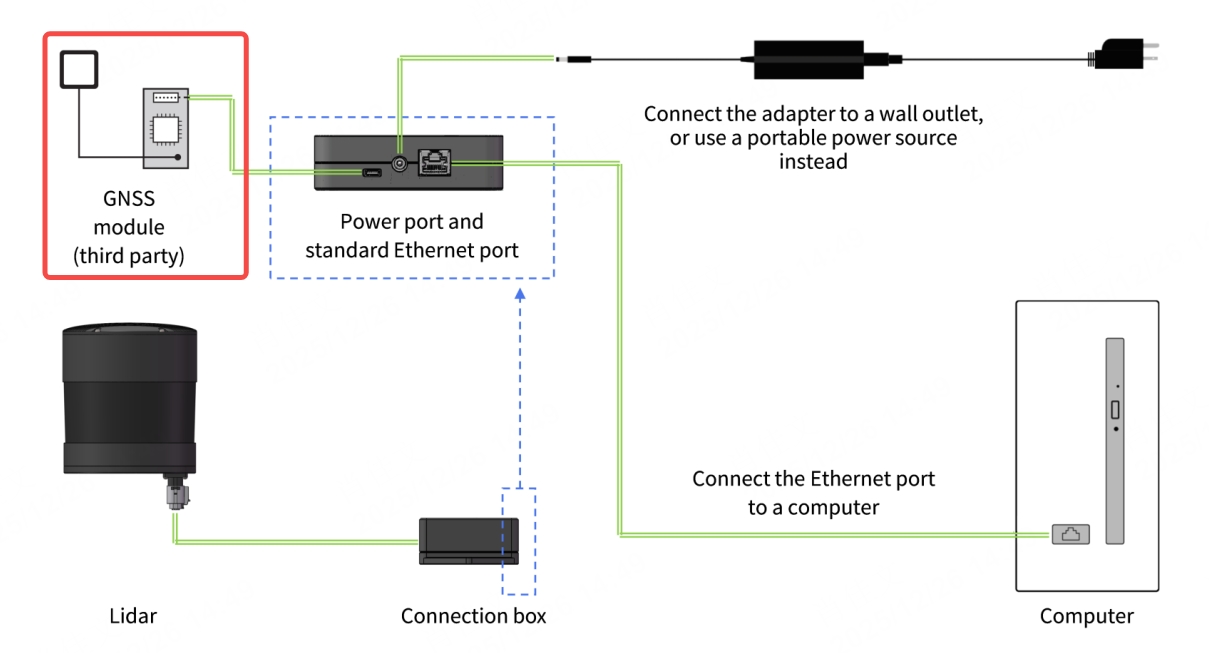
2.1.2 JT16
- Pin definitions on the lidar side:
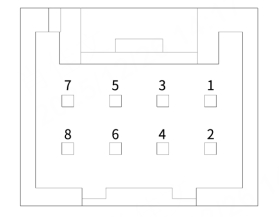
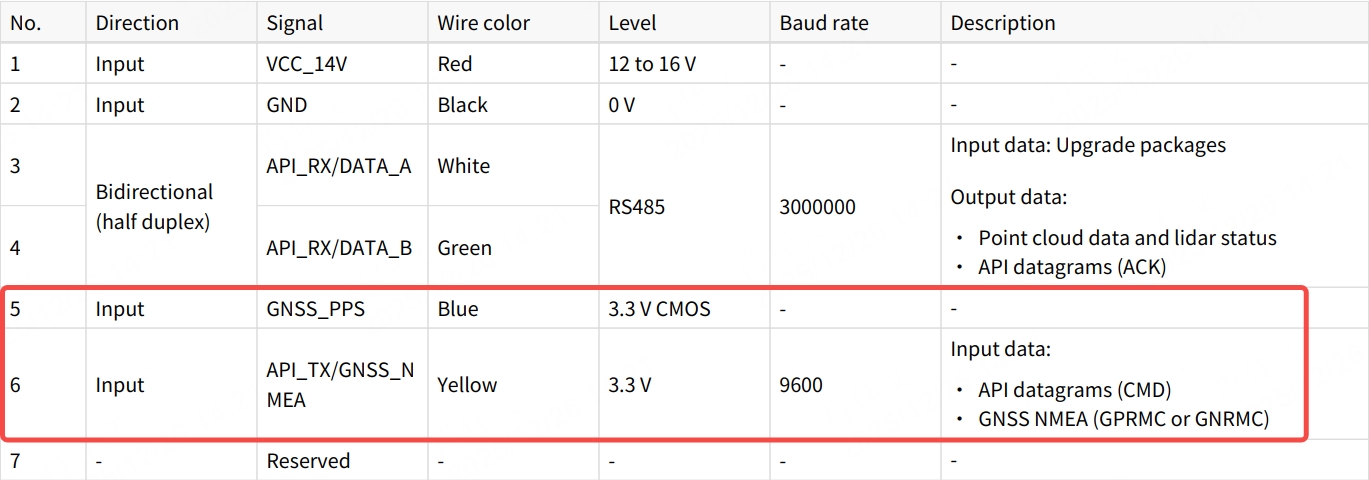
- Pin definitions on the connection box side (if used):
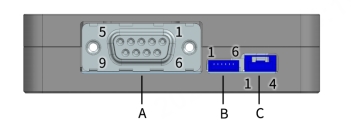
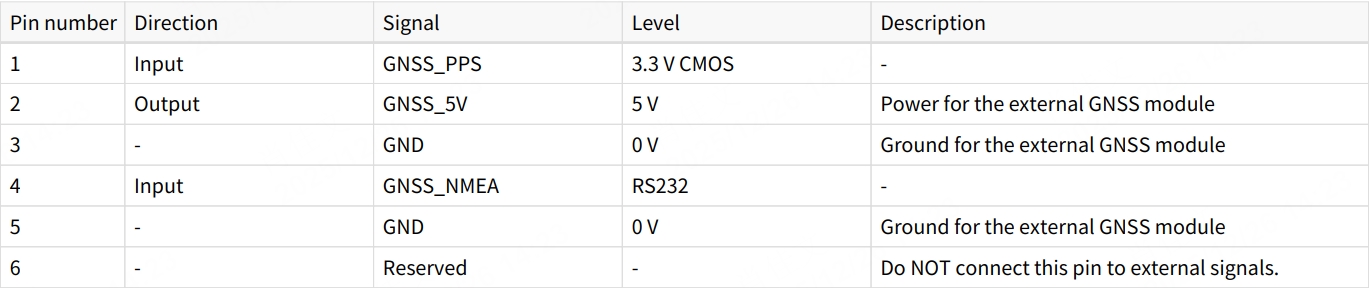
- If the connection box is connected to the GNSS module, refer to the hardware connection diagram below:
2.2 Lidar Parameter Configuration
2.2.1 Pandar128
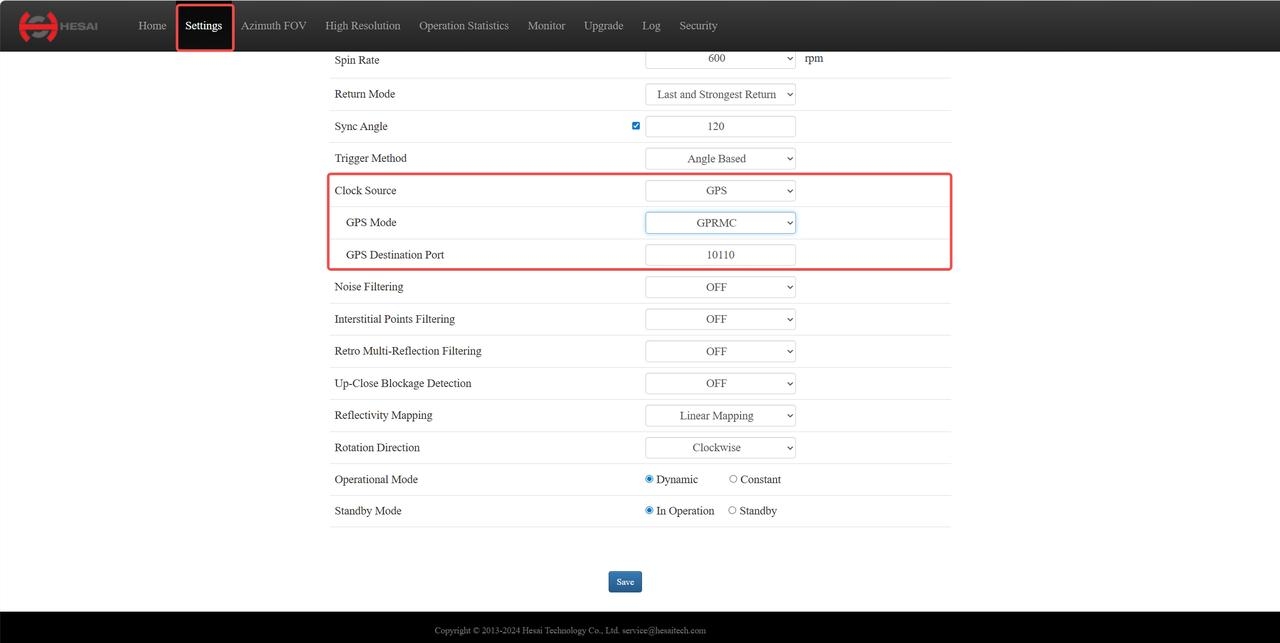
- Log in to the web interface using the lidar's IP address.
- Go to the [Settings] page, set [Clock Source] to
GPS, [GPS Mode] toGPRMCorGPGGA, and configure the [GPS Destination Port] (default value:10110).
2.2.2 JT16
JT16 does not require time synchronization parameter configuration. It only supports GPS time synchronization by default.
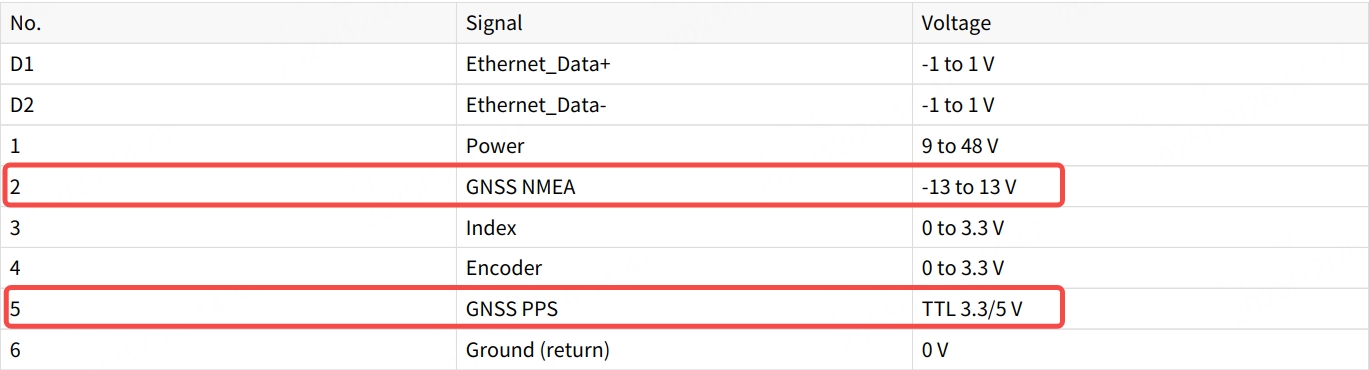
2.3 GNSS Signal Electrical Requirements
2.3.1 Signal Level Requirements
| GNSS_PPS | GNSS_NMEA | |
|---|---|---|
| Pandar128 | TTL 3.3V/5V | -13~13V (RS232 level at connection box) |
| JT16 | CMOS 3.3V | 3.3V (RS232 level at adapter box) |
Notes:
1. When connecting or disconnecting GNSS signals from the GNSS pins on the Pandar128 cable or plugging/unplugging the GNSS module from the connection box, please ensure the lidar is powered off.
2. If operating the Pandar128 while powered on, discharge static electricity first and avoid directly touching the GNSS port or pins.
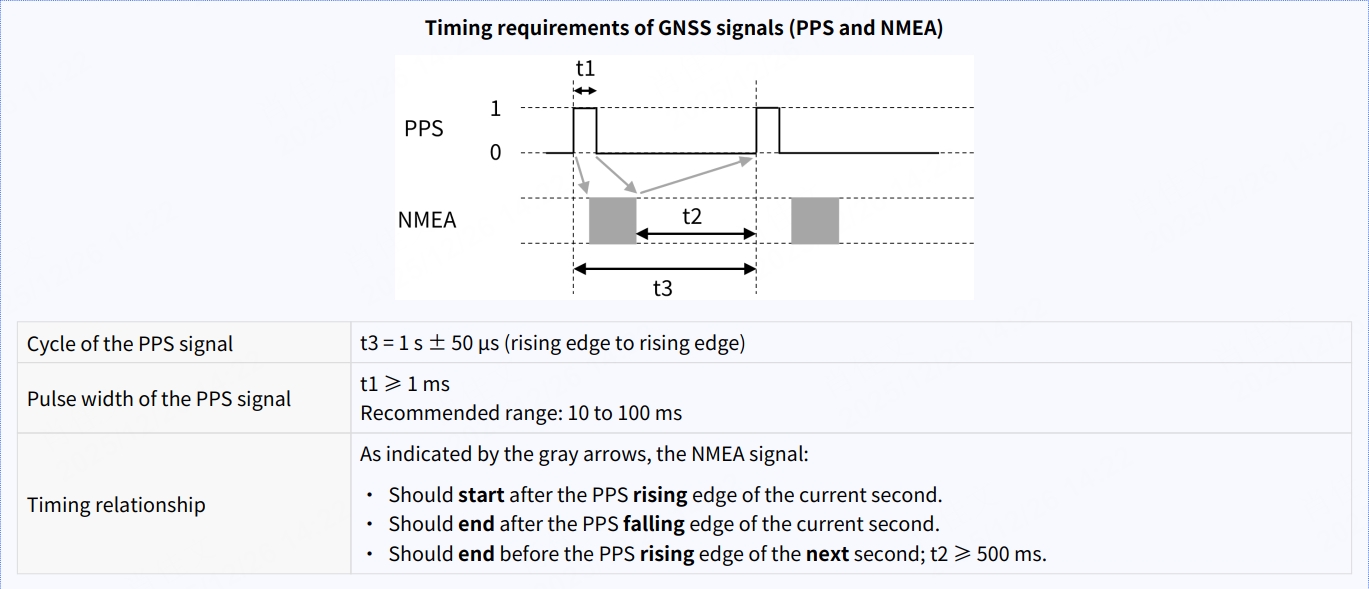
2.3.2 Signal Time Sequence Requirements
The time sequence requirements for GNSS PPS and NMEA signals are the same for Pandar128 and JT16, as described below:
2.4 GNSS Signal Status and Lidar Time Update Rules
2.4.1 Pandar128
Each rising edge of the internal 1Hz PPS signal in Pandar128 triggers a GPS data packet containing received GNSS signal data, including UTC time, positioning signal status, etc. The PPS and NMEA signal statuses and corresponding lidar time update rules are described below:
| PPS / NMEA Status | Date and Time | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Unlock (Initial) | Virtual Value | Starts from a virtual UTC time (e.g., 2000-01-01 00:00:00), incremented by the internal 1Hz signal. |
| Locked | Synchronized | The rising edge of the internal 1Hz signal aligns with the PPS pulse, extracting the previous second's NMEA data. |
| Unlock (Lost) | Internal Timing | Time increments from the last synchronized moment, resulting in drift compared to real GNSS time. |
2.4.2 JT16
JT16 does not output GPS data packets. When the point cloud time matches the system time, it indicates that GPS time synchronization is successful; otherwise, it starts from a virtual UTC time and increments based on the lidar's internal 1Hz signal.
3 GPS Time Synchronization Results
3.1 Pandar128
The timestamp information in the point cloud UDP data is located at the end of the data, occupying 10 bytes, including the date, time (the whole second part of UTC time), and the microsecond part of UTC time.

The parsed UTC time result is: 2025-12-23 20:17:39.423224.
3.2 JT16
Using Hesai's official ROS driver, the point cloud timestamp can be printed directly in the terminal. When GPS synchronization is successful, the timestamp matches the system time.
The timestamp information in the point cloud data is located in the data header, occupying 10 bytes, including the date, time (the whole second part of UTC time), and the microsecond part of UTC time.
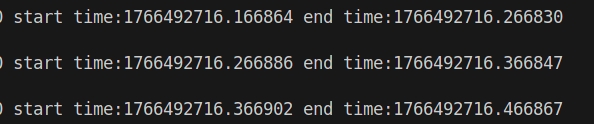
The parsed UTC time result is: 2025-12-23 20:25:16.166864.
Note: The integer part of the timestamp data in the figure (1766492716) corresponds to the Unix format time of the whole second part of UTC time, which is the total number of seconds accumulated since UTC time (Coordinated Universal Time) 00:00:00 on January 1, 1970.
4 Common GPS Time Synchronization Issues Troubleshooting
4.1 Unlock GNSS Signal Status in lidar
- Ensure the GNSS device is properly connected (refer to the Hardware Connection section).
- Verify that the PPS signal is input to the lidar.
- For Pandar128, confirm that the [GPS Destination Port] is correctly configured via the web interface or TCP commands.
- Ensure the GNSS signal meets the electrical requirements of the lidar and connection box.
- Power cycle the lidar and check if the issue is resolved.
If the lidar still cannot achieve GPS time synchronization after following the above steps, contact Hesai technical support.
Find it useful?