Use Serial API
1 Overview
Some Hesai lidar models support communication with a computer host using Serial API commands. These commands are sent via the RS232 protocol as command datagrams (CMD datagram) and received via the RS485 protocol as acknowledgment datagrams (ACK datagram). This enables control, operation, and query functionalities for the lidar.
Note: The current Serial API commands are only applicable to the JT16 lidar. For detailed command information, please refer to the JT16 Serial API Manual.
2 Application Instructions
The application and basic operation steps for Serial API commands are as follows:
-
Connect the lidar to the host and ensure that communication is successfully established (refer to Configure Serial Port for details).
-
Send API commands from the host to the lidar via the serial port, receive responses from the lidar, and parse the responses according to the API manual to confirm whether the API command was successfully executed.
2.1 Query Serial Port
2.1.1 Windows Systems
If using a Windows system, open "Device Manager" to view the ports.
To distinguish between serial ports, user can first insert the RS485 cable into the USB port and note the port number, then insert the RS232 cable and note the newly recognized port number.

2.1.2 Ubuntu Systems
If using an Ubuntu system, user can enter the following command in the terminal to view the current ports:
ls /dev/ttyUSB*
To distinguish between serial ports, first insert the RS485 cable into the USB port and note the port number, then insert the RS232 cable and note the newly recognized port number.
Note:
- On Ubuntu, the full port name is
/dev/ttyUSB*. When connecting via a script, the full name must be entered. - If the connection fails due to insufficient permissions, enter the following command to grant the necessary permissions:
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyUSB*
Pleaes refer to the Configure Serial Port - Process section for detailed instructions.
2.2 Serial API Data Structure
2.2.1 CMD Datagram Data Structure
The host sends command datagrams (CMD datagram) to the lidar via RS232 communication. The data structure of the command datagram is shown below:
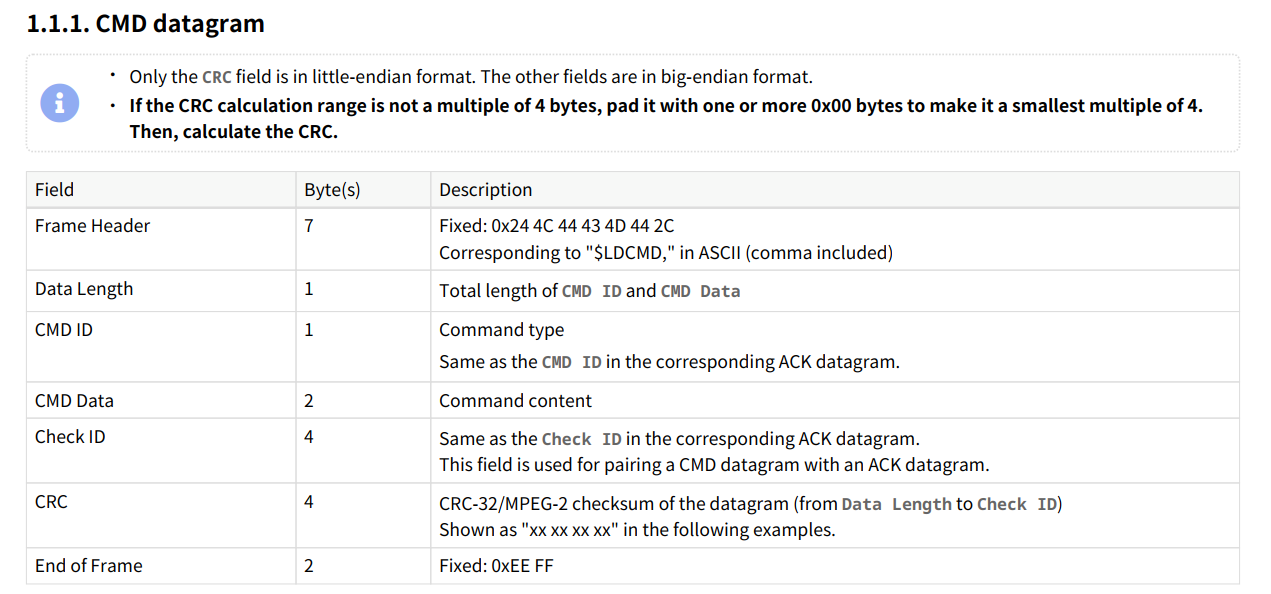
The CRC checksum uses the CRC-32/MPEG-2 algorithm, calculated from the "Data Length" to "Check ID" fields. Users can calculate the CRC using online CRC tools or the script provided here from this document. The CRC result is filled into the command datagram in little-endian format (low byte first).
2.2.2 ACK Datagram Data Structure
After the command datagram (CMD datagram) is sent, the host receives acknowledgment datagrams (ACK datagram) from the lidar via RS485 communication. The data structure of the acknowledgment datagram is shown below:

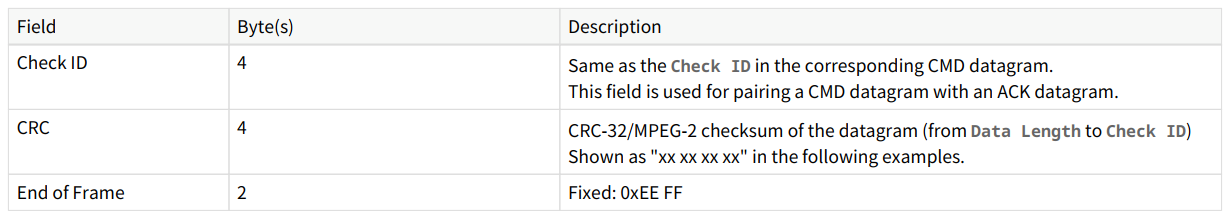
Note: Similar to command datagrams, point cloud packets are also transmitted via RS485 communication. Users need to filter acknowledgment datagrams (ACK datagram) from the RS485 data stream based on the "Frame Header" and "End of Frame" fields. Parse the "Fault Code" field in the acknowledgment datagram. If the field is 0, the command was successfully executed. If it contains other values, refer to the "Description" section of the field from the image above for troubleshooting.
3 Examples
This document introduces two different methods for sending Serial API commands, along with corresponding examples. Users can choose one based on their actual needs.
Note: Before using Serial API commands, refer to the product manual to confirm that the command configuration is valid for the lidar being used.
3.1 Use LidarUtilities to Send Serial API Commands
Refer to the Use LidarUtilities document for information on obtaining and using the LidarUtilities software.
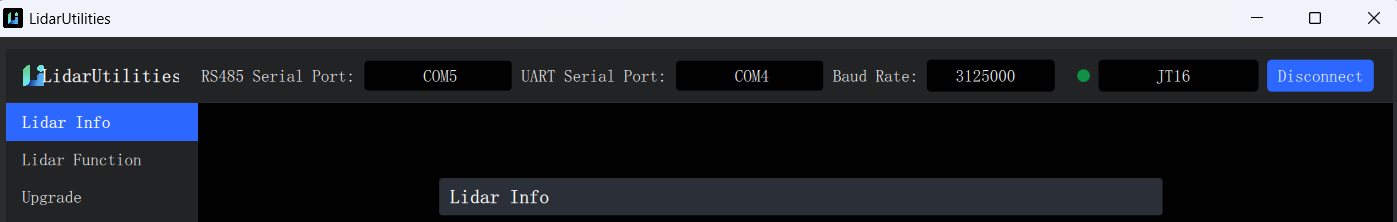
Power on the JT16 lidar and connect it to the host. For example, on a Windows system, open LidarUtilities, select the product model as JT16, configure the RS485 port, RS232 port, and baud rate (note: the standard baud rate is 3000000, and the non-standard baud rate is 3125000; if unsure, try both), and click "Connect." Once connected successfully, the interface will appear as shown below:
For example, to send a command to set the motor speed, the specific configuration parameters for the command datagram are shown below:
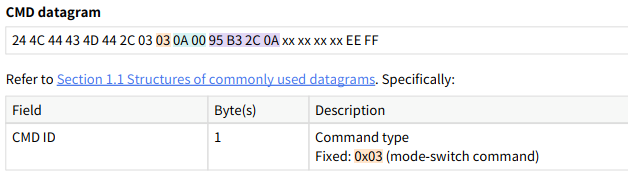
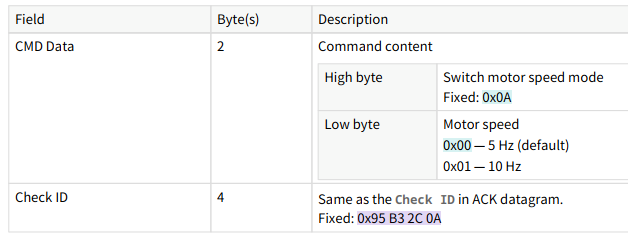
Note: For detailed command instructions, refer to the "2.2 Switch motor speed" section of the JT16 API manual.
The method for sending serial commands is shown below:
- Switch to the "Send Serial Command" page.
- In the "Send Command - Command Code" section, enter
03(CMD ID). - In the "Payload" section, enter
0A 01(CMD DATA, 10Hz), leaving a space between the values. - Click "Send" to send the command.
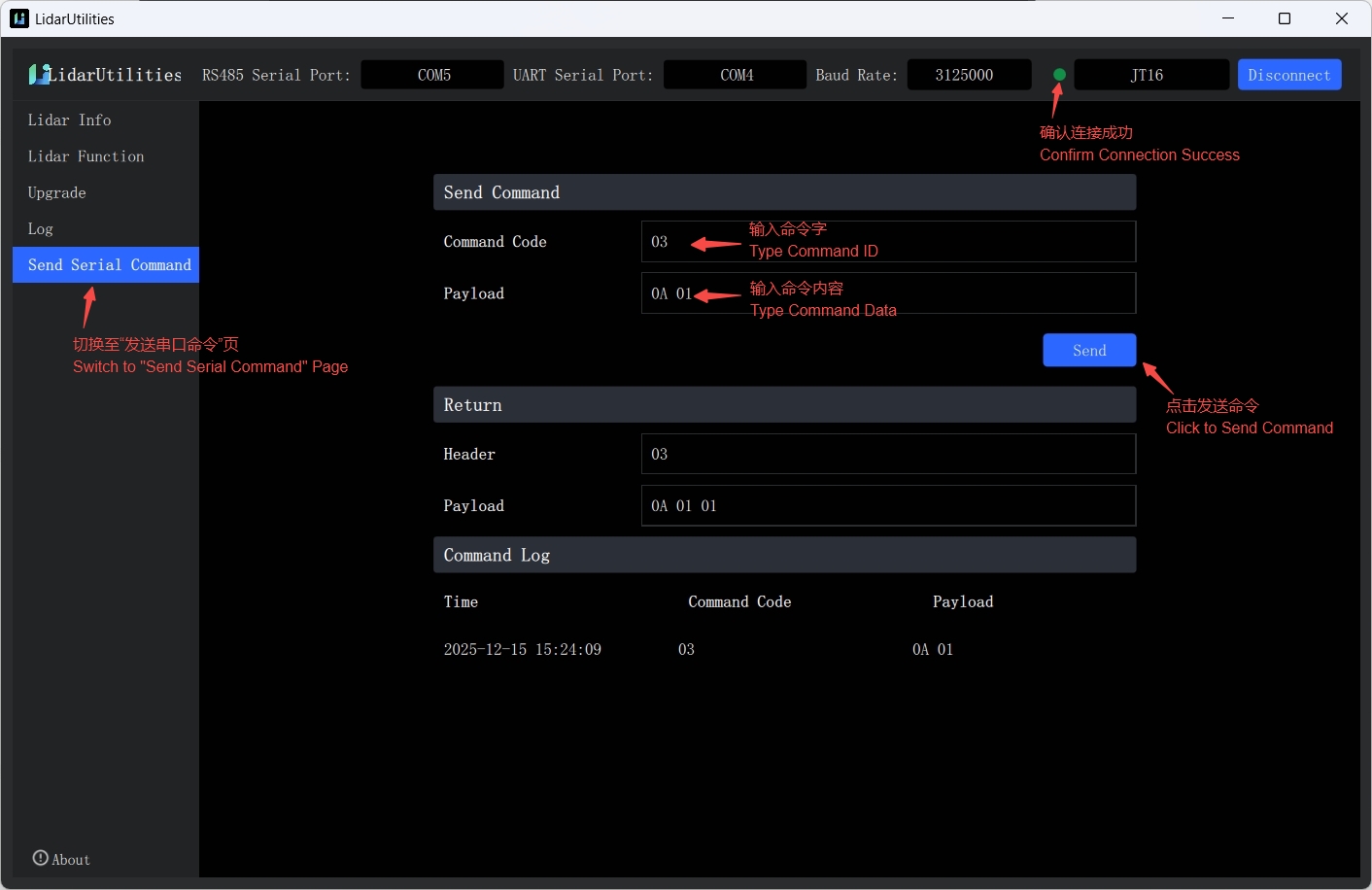
Note: This command is only provided as an example. Since JT16 currently does not support setting the motor speed to 10Hz, the "Fault Code" in the ACK datagram will display 1. While for any supported commands, the expected "Fault Code" in the acknowledgment datagram should be 0.
3.2 Use a Script to Send Serial API Commands
Similarly, to send a command to set the motor speed, users can use the following python script to perform the corresponding operation. The script primarily handles CMD command packaging and sending. After configuring the RS232 port, baud rate, command ID, and command content, the script will automatically calculate the data length and CRC checksum, complete the packaging, and send the command. Users can verify whether the command was successfully executed by checking the expected effect or capturing the ACK datagram and examining the "Fault Code" field.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# """
# - Simplified version: build and send CMD frame only (no ACK listening)
# - Configurable CMD parameters, compute CRC32/MPEG-2 (little-endian)
# """
import serial
# -------------------- USER CONFIGURATION AREA --------------------
# Serial settings
RS232_PORT = "COM4" # RS232 port
RS232_BAUD = 9600 # RS232 baud rate
# RS485_PORT = "COM5" #RS485 port
# RS485_BAUD = 3000000 # RS485 baud rate
# CMD parameters
CMD_ID = 0x03 # Command ID
CMD_DATA = bytes.fromhex('0A 01') # Command data segment
# -------------------- USER CONFIGURATION AREA --------------------
# Frame constants--------------------------------------------------
CHECK_ID = bytes.fromhex('95 B3 2C 0A') # 4-byte check ID
FRAME_HEADER_CMD = b"\x24\x4C\x44\x43\x4D\x44\x2C" # CMD header
FRAME_END = b"\xEE\xFF" # Frame tail
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# -------------------- CRC32/MPEG-2 CALCULATION -----------------
def init_crc32_mpeg2_table() -> list[int]:
# """Initialize CRC32/MPEG-2 lookup table"""
crc_table =[0]*256
for i in range(256):
crc = i << 24
for _ in range(8):
crc = (crc << 1) ^ 0x04C11DB7 if crc & 0x80000000 else crc << 1
crc_table[i] = crc & 0xFFFFFFFF
return crc_table
CRC_TABLE = init_crc32_mpeg2_table()
def crc32_mpeg2(data: bytes) -> int:
# """Compute CRC32/MPEG-2 checksum (unsigned 32-bit)"""
if not data:
return 0xFFFFFFFF
crc = 0xFFFFFFFF
for b in data:
crc = ((crc << 8) ^ CRC_TABLE[(crc >> 24) ^ b]) & 0xFFFFFFFF
return crc
def build_cmd(cmd_id: int, cmd_data: bytes, check_id: bytes) -> bytes:
# """
# Automatically build CMD frame (with CRC)
# :param cmd_id: Command ID (1 byte)
# :param cmd_data: Command data segment
# :param check_id: 4-byte check ID
# :return: Complete CMD frame (header + payload + CRC + tail)
# """
# 1. Build base payload (length + CMD_ID + CMD_DATA)
data_len = 1 + len(cmd_data) # CMD_ID(1 byte) + CMD_DATA length
payload = bytes([data_len, cmd_id]) + cmd_data
# 2. Align to 4-byte boundary (whole payload + check_id)
total_payload_len = len(payload) + len(check_id)
pad_len = (4 - total_payload_len % 4) % 4
payload += b"\x00" * pad_len
# 3. Append CHECK_ID
payload += check_id
# 4. Compute CRC (little-endian)
crc_value = crc32_mpeg2(payload)
crc_bytes = crc_value.to_bytes(4, byteorder="little") # low byte first
# 5. Assemble full frame
full_cmd = FRAME_HEADER_CMD + payload + crc_bytes + FRAME_END
return full_cmd
# -------------------- MAIN (construct + send CMD only) ---------
def main():
# 1. Build CMD frame
try:
cmd_frame = build_cmd(CMD_ID, CMD_DATA, CHECK_ID)
print("========== Build CMD frame ==========")
print(f"Hex: {cmd_frame.hex(' ').upper()}")
print(f"Length: {len(cmd_frame)} bytes")
print("=========================================")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to build CMD frame: {e}")
return
# 2. Send CMD frame (RS232)
try:
with serial.Serial(
port=RS232_PORT,
baudrate=RS232_BAUD,
timeout=1,
parity=serial.PARITY_NONE,
stopbits=serial.STOPBITS_ONE,
bytesize=serial.EIGHTBITS
) as ser_232:
ser_232.reset_input_buffer()
ser_232.reset_output_buffer()
ser_232.write(cmd_frame)
ser_232.flush()
print("CMD frame sent")
except serial.SerialException as e:
print(f"Failed to send CMD frame: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Note: This script is only provided as an example. JT16 currently does not support setting the motor speed to 10Hz.
Find it useful?