Use SLAM
1 Overview
When a robot moves in an unknown environment, it needs to determine its motion state and build a representation of the surrounding environment (which can be landmarks or a map). By using the SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) algorithm, the robot can achieve localization (determining its motion state) while simultaneously building a map (mapping), helping the robot understand its surroundings.
2 Application Method
This document uses Hesai's JT128 lidar as an example to briefly introduce the application method of the open-source SLAM algorithm DLIO.
-
JT128 is a compact 360° x 189° ultra-hemispherical 3D lidar designed for robotics and industrial applications. It features a resolution of 0.4° (H) x 0.74° (V) and a built-in IMU, making it suitable for integration into mobile robots for perception and mapping tasks (see here for more information about JT128).
-
DLIO is a lightweight lidar-inertial odometry SLAM open-source algorithm that can be adapted to support various lidar data formats. For a detailed introduction and access to this algorithm, see Direct Lidar-Inertial Odometry (DLIO).
Detailed Steps to run DLIO with JT128:
- Configure the ROS environment (refer to ROS Environment Setup).
Note: It is recommended to install and use ROS Noetic.
-
Follow the installation and compilation instructions in the readme files of DLIO and Hesai ROS Driver.
-
Properly connect the lidar and configure the Hesai ROS driver.
Note: If IMU data is included and used in the application, user needs to configure send_imu_ros: true in the config.yaml file and verify whether the driver is correctly sending IMU data and point cloud data following the method as shown below:
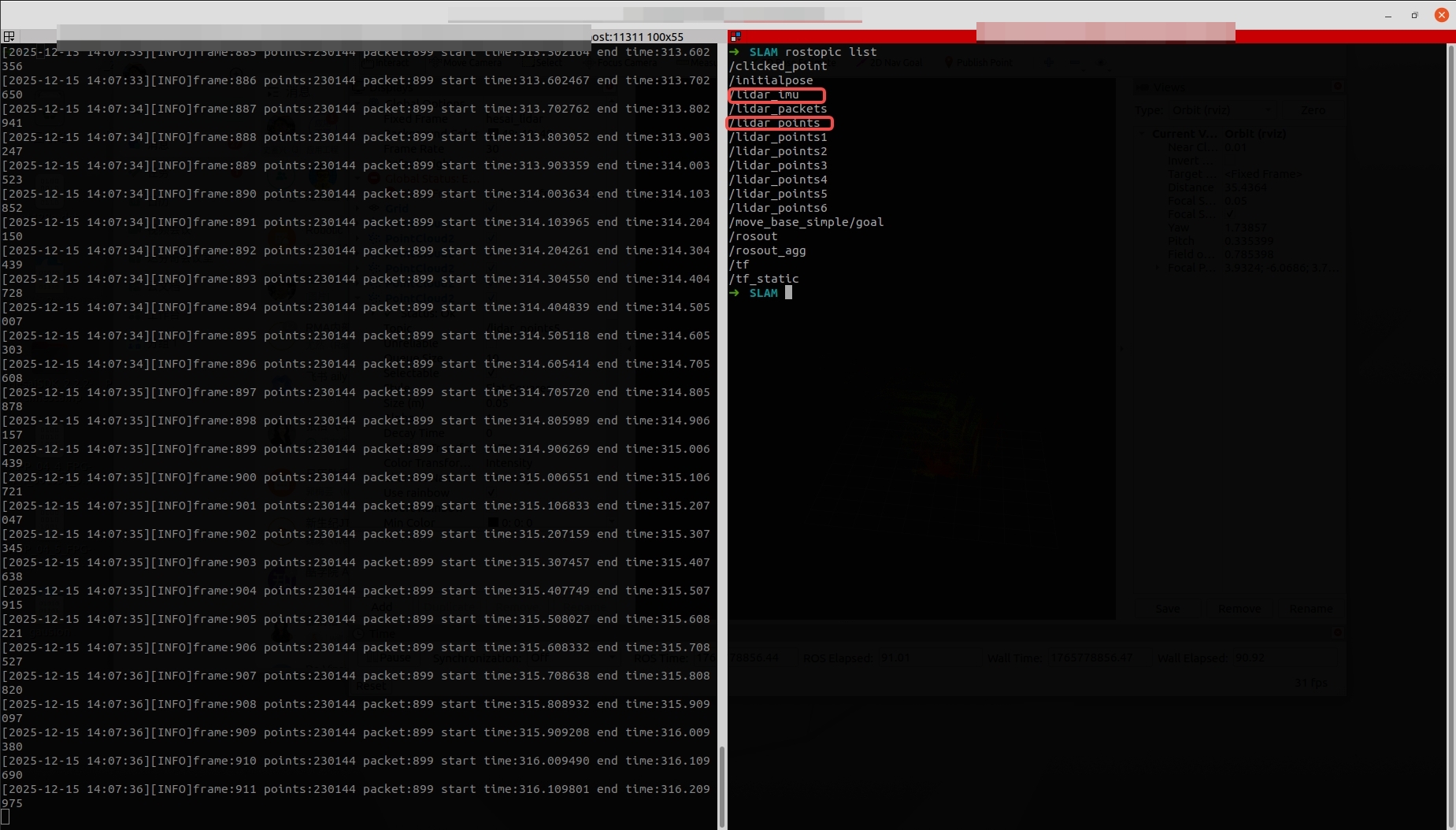
- Open another terminal and run the following command to execute the DLIO algorithm:
roslaunch direct_lidar_inertial_odometry dlio.launch \
rviz:=true \
livox_topic:=/lidar_points \
imu_topic:=/lidar_imu
3 SLAM Results Demonstration
The SLAM results of JT128 after running the DLIO algorithm are illustrated with the below example:
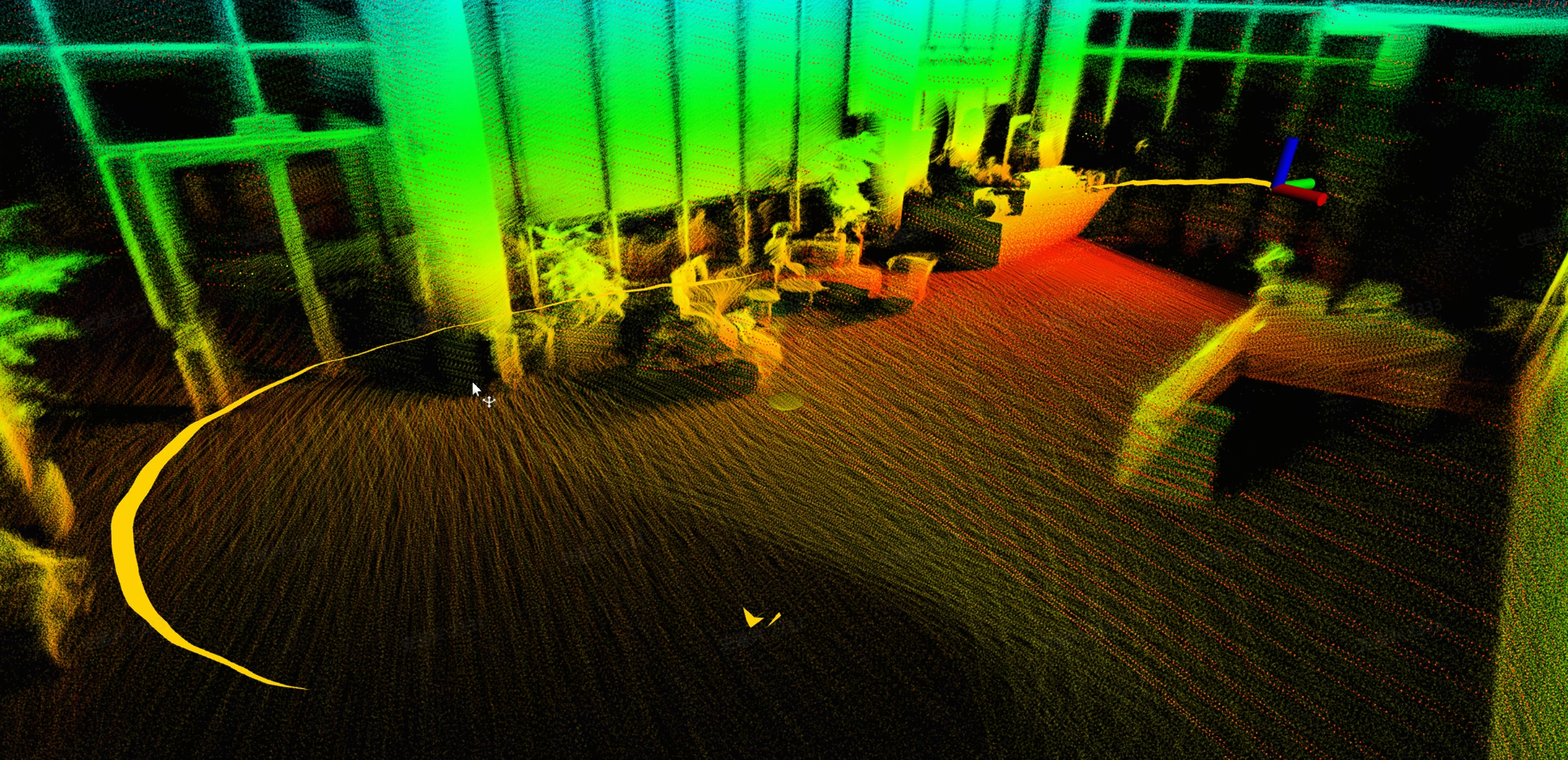
This algorithm can output the current pose, historical trajectory, and point cloud map based on the lidar point cloud and IMU data. User can also use the following command to export the point cloud map in .pcd format:
rosservice call /robot/dlio_map/save_pcd LEAF_SIZE /path/to/your/directory
Find it useful?