Reflectivity
1 Overview
Reflectivity is one of the key parameters in lidar applications. It has a significant impact on evaluating the detection performance, point cloud data accuracy, and target recognition capability of lidar.
2 Definition
Reflectivity generally refers to the ratio of the radiant energy reflected by the surface of an object to the total radiant energy incident on the object. In optics, the direction of light reflection generally follows two modes (as shown in the figure below):
- Specular Reflection, where the reflected light is emitted in a single fixed direction determined by the incidence angle of the incident light;
- Diffuse Reflection, where the reflected light is emitted in all directions facing the object.
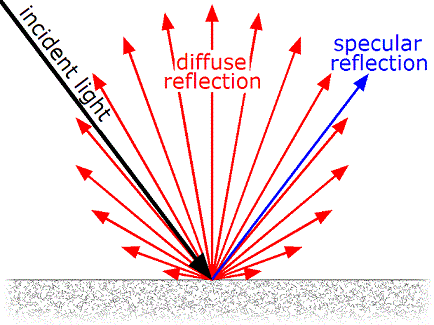
For objects with uniformly distributed reflected energy intensity in all directions, they are defined as Lambertian Reflectors. Regarding lidar, the defined reflectivity particularly applies to such type of target objects. In real-world applications, most objects approximate Lambertian reflectors, meaning their reflectivity is an inherent property determined by their material and surface characteristics, while unaffected by the direction of laser incidence and reflection during detection.
Below are the reflectivity values of common materials in nature:
| Common Objects | Reflectivity |
|---|---|
| Black Cloth | 2~3% |
| Black Plastic | 15% |
| Wood | 20% |
| Newspaper | 55% |
| White Cardboard | 90% |
| Glossy Metal Surface | 150% |
| High-Reflectivity Signs | >300% |
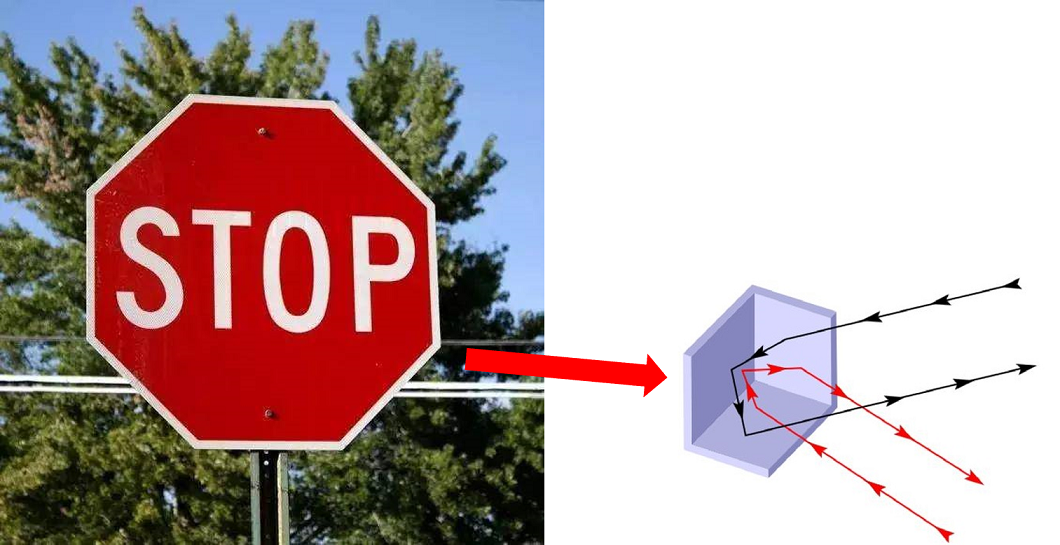
Note: Extremely high-reflectivity road signs, also known as retro-reflectors, have special surface structures that can cause specular reflection for incident light from any directions (see the diagram below). These objects are not Lambertian reflectors. Since the reflectivity used by lidar is based on diffuse reflection calibration of standard Lambertian reflectors (reflectivity < 100%), then the objects showing specular reflection effects (including retro-reflectors, shiny metals, etc.) may exhibit reflectivity far exceeding that of common diffuse reflectors, usually exceeding 100%.
3 Influencing Factors
The factors affecting the reflectivity of an object mainly include:
-
Material Properties: Surface roughness (rough surfaces cause diffuse reflection, leading to lower reflectivity compared to smooth surfaces), color, and absorption rate (dark materials, such as black paint, absorb more laser energy, resulting in lower reflectivity);
-
Environmental Conditions: Humidity (moisture increases surface reflectivity), temperature (thermal expansion of metallic materials may alter their surface properties), etc.
4 Application Scenarios
Various lidar application scenarios rely on reflectivity information. For example, in ADAS or L4 autonomous driving solutions, lidar is used to construct a real-time 3D map of the environment. Reflectivity can help distinguish and identify targets of different materials, improving the system's environmental perception capability and efficiency. Below are two typical cases where reflectivity is used for environmental perception and target recognition:
4.1 Lane Line Recognition
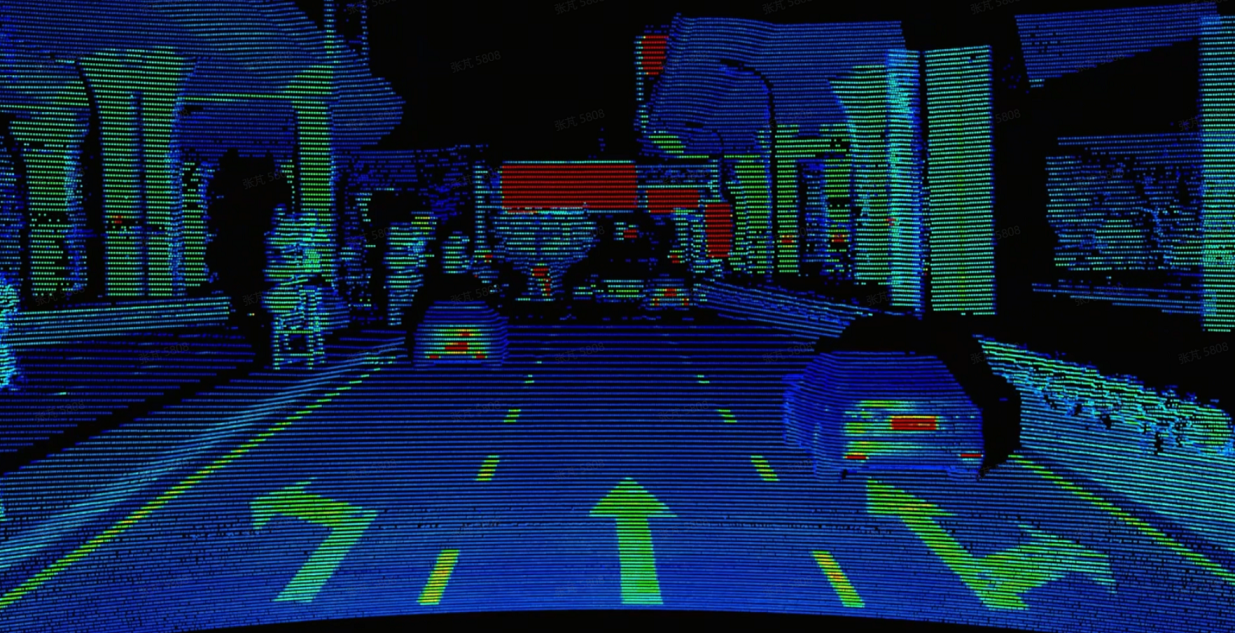
Recognizing lane lines during highway driving is crucial for autonomous driving road planning and control. In high-precision mapping scenarios, lane line recognition mainly relies on the contrast and distinction between the reflectivity of lane lines and asphalt roads. Since mapping involves collecting large amounts of data on highways using mapping vehicles and then automatically labeling lane lines with software, if lane lines are significantly distinguishable from regular road surfaces, the software can quickly and accurately identify and map them, greatly reducing the time and cost of the labeling process. The AT128 sample point cloud below shows a clear distinction between lane lines and lane markings.
4.2 High-Reflectivity Object Recognition
Common road signs are often high-reflectivity objects, with reflectivity typically reaching the upper limit of lidar measurement. By using reflectivity information output by lidar, road signs can be identified in time, and the vehicle control system can direct cameras to focus on the specific information on the signs, enabling efficient planning and control of vehicle driving behavior.
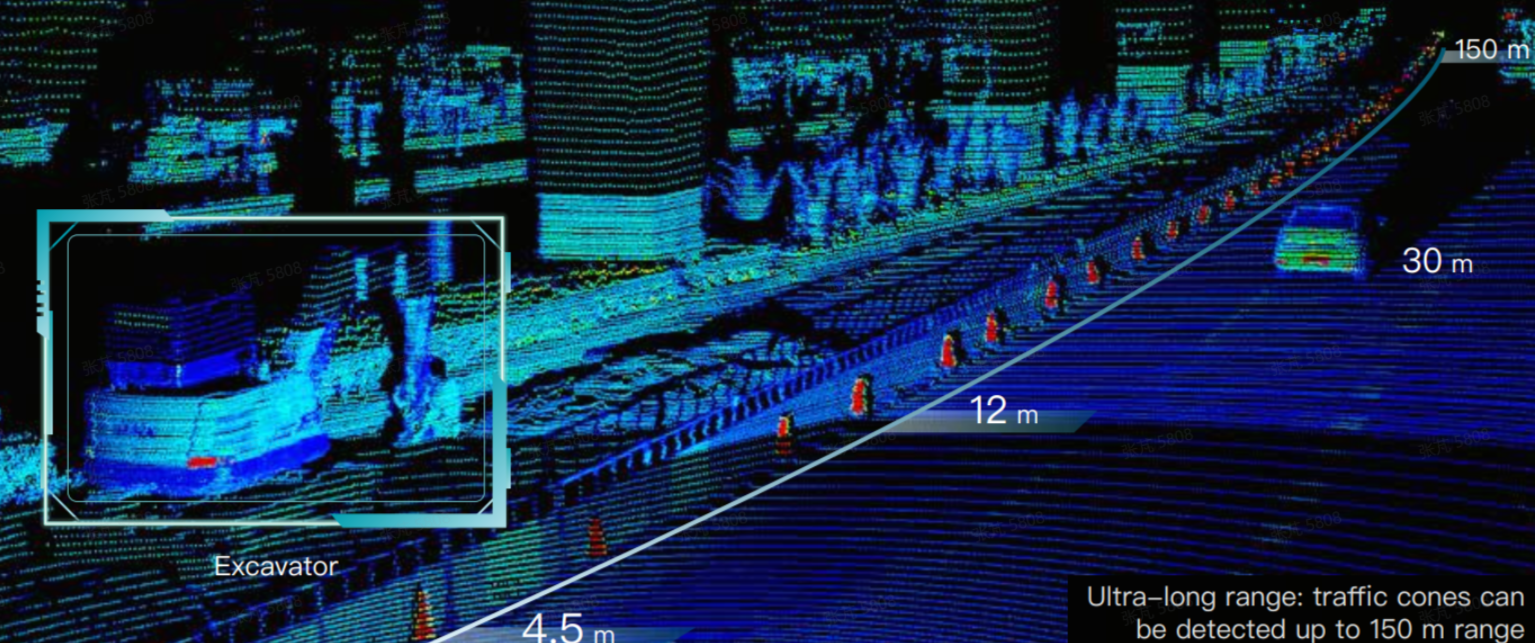
Additionally, in some construction site scenarios, high reflectivity cones are often used for marking. If high reflectivity cones can be quickly identified and distinguished at the farthest possible distance, the vehicle control system can intervene early and execute corresponding decisions such as deceleration or lane changes. This significantly enhances the safety and comfort of autonomous driving. The image below shows the recognition performance regarding roadside cones in Pandar128.
Find it useful?