Acquire Angle Correction File
1 Overview
The angle correction file serves as the directional reference for system calibration, point cloud calculation, and spatial positioning. To ensure measurement accuracy, Hesai performs independent angle calibration for each Lidar unit during manufacturing. The calibration results are unique for each unit, and this unique correction data is recorded as the "angle correction file" which is provided within the Lidar.
Lidar connection methods include Ethernet connection and serial port connection. The angle correction file formats include CSV format and DAT format. Please refer to the table below for specific models.
Lidar Models and Connection Methods Table:
| Connection Method | Ethernet Connection | Serial Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Product Series | Pandar, OT, QT, XT, AT, FT, JT | JT |
| Applicable Models | Pandar40P, Pandar64, Pandar128E3X, OT128, QT64C1X, QT128C2X, XT32, XT16, XT32M2X, AT128E2X, AT128P, ATX, FTX, JT128 | JT16 |
Lidar Models and File Formats Table:
| File Format | CSV Format | DAT Format |
|---|---|---|
| Product Series | Pandar, OT, QT, XT, JT | AT, JT, FT |
| Applicable Models | Pandar40P, Pandar64, Pandar128E3X, OT128, PandarQT, QT128C2X, XT32, XT16, XT32M2X, JT128 | AT128E2X, AT128P, ATX, JT16, FTX |
2 Application Instructions
2.1 Using PandarView2
2.2 Using API Commands
2.2.1 Ethernet Connection
CSV Format
DAT Format
2.2.2 Serial Port Connection
Serial Port Connection
This document provides examples of how to obtain the angle correction file using the two methods mentioned above. You can choose one or more methods based on your actual situation.
3 Examples
Note: The following examples are based on the user and command manuals for XT32, AT128P, and JT16. The configuration of different Lidar models may vary. Please refer to the user manual for the specific model.
3.1 Acquiring Angle Correction File Using PandarView2
-
Visit Hesai's official website to download and install the PandarView2 client.
-
Connect the Lidar to the computer host and ensure that communication is successfully established between the Lidar and the host. (For Ethernet connection methods, refer to How to Configure Ethernet; for serial port connection methods, refer to the relevant Lidar user manual.)
-
Open PandarView2, click the [Listen for Data] button in the top-left toolbar. The Lidar connection methods include Ethernet connection and serial port connection, and the configuration methods differ slightly. Fill in the parameters according to the actual Lidar configuration.
Note: For serial port connections, the PandarView2 version must be greater than 2.1.7. Select the Serial Port option in the popout window and fill in the RS485 serial port address and baud rate. Reference model: JT16.
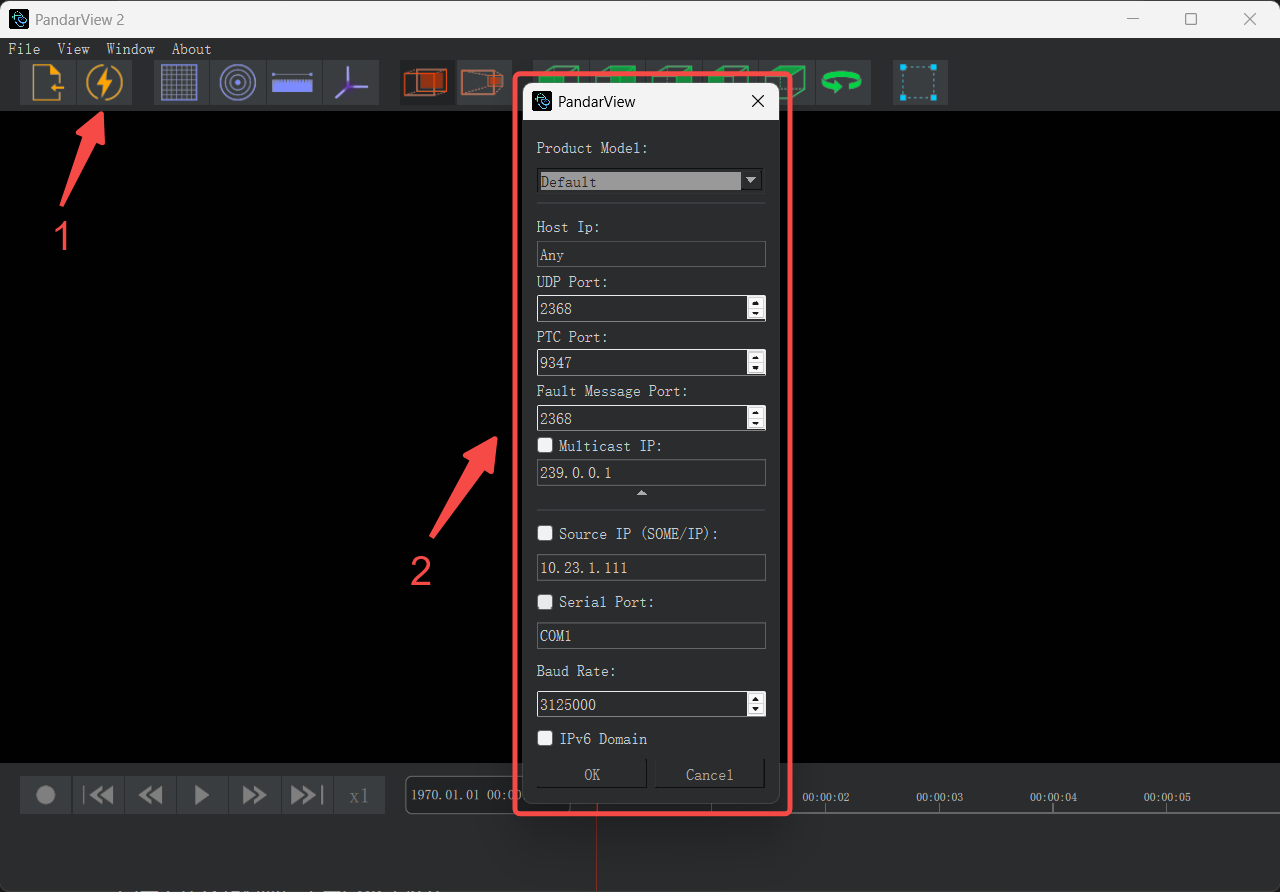
After completing the parameter configuration, click [OK] to confirm.
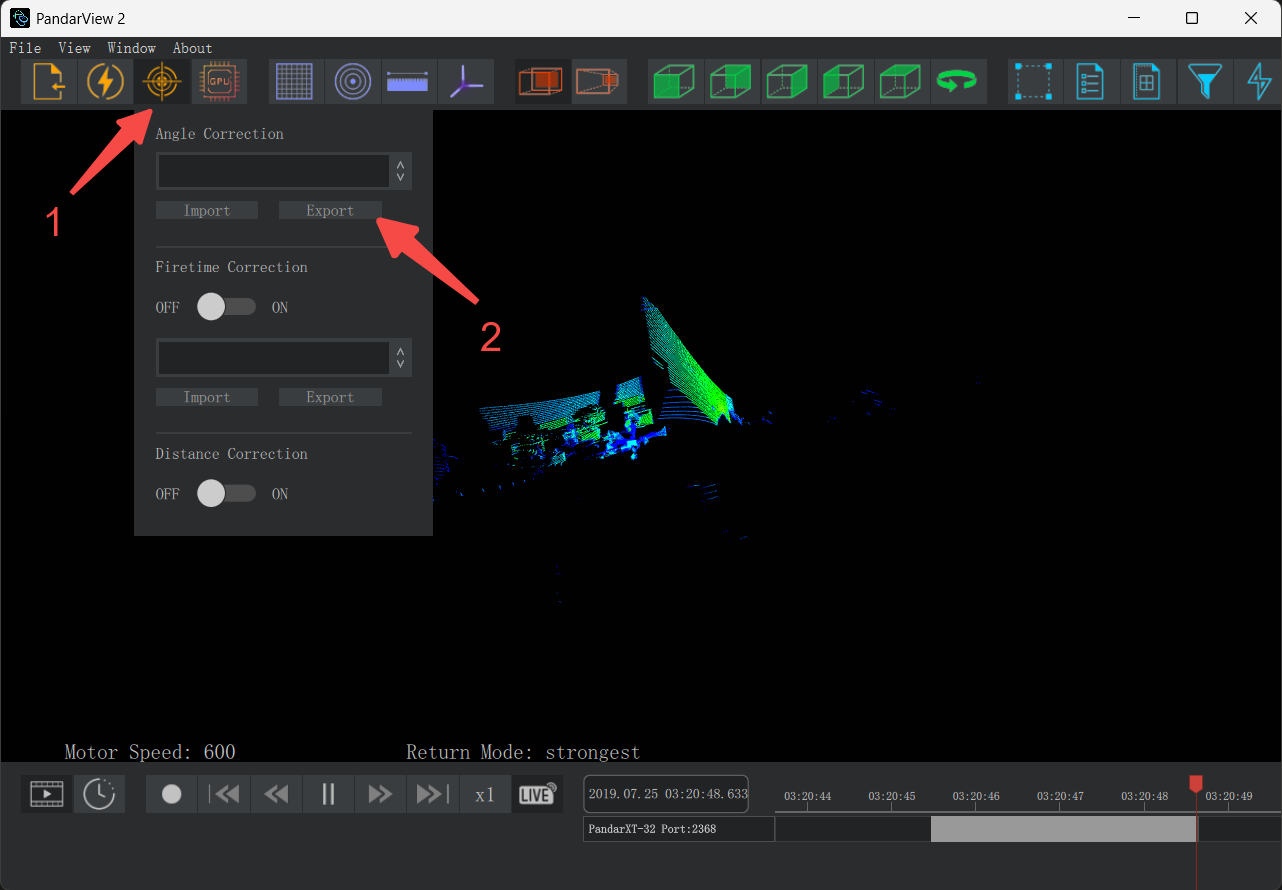
- Click the [Correction] button in the toolbar, go to the Angle Correction section, and click 'Export'. In the popup window, enter the file name, select the save location, and click 'Confirm' to complete the export.
Note: When saving files on Ubuntu systems, you must add the correct file format extension (.csv/.dat).
3.2 Acquiring Angle Correction File Using API Commands
3.2.1 Ethernet Connection
3.2.1.1 CSV Format
Reference Model: XT32
- After connecting the Lidar to the host, open the script below using an IDE:
import socket, ssl, pprint, time
import random
import struct
default_host = "192.168.1.201" # Change this to your Lidar IP
default_port = 9347 # Change this to your Lidar PTC Port
class PTC:
def __init__(self, host=default_host, port=default_port):
self.s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
lp = random.randint(10000, 30000)
self.s.bind(('0.0.0.0', lp))
self.s.settimeout(30)
self.s.connect((host, port))
def closeSocket(self):
self.s.shutdown(1)
# self.s.close()
def ByteToHex(self, h):
return ''.join(["%02x" % x for x in h]).strip()
def read_bytes(self, payload_size):
chunks = []
bytes_received = 0
while bytes_received < payload_size:
chunk = self.s.recv(payload_size - bytes_received)
if chunk == b"":
raise RuntimeError("Socket has been unexpectedly closed")
chunks.append(chunk)
bytes_received = bytes_received + len(chunk)
return b"".join(chunks)
def sender(self, cmd_code, payload):
"""
:param cmd_code:
:param payload: payload should input like '015d010207'
:return:
"""
if cmd_code in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e',
'f']:
cmd_code = "0" + str(cmd_code)
print("payload :")
print(payload)
if not payload or payload.upper() == "NONE":
payload_len = 0
p = '4774' + str(cmd_code) + "00" + struct.pack('>L', payload_len).hex()
else:
payload_len = len(bytes.fromhex(payload))
p = '4774' + str(cmd_code) + "00" + struct.pack('>L', payload_len).hex() + payload
data = bytes.fromhex(p)
self.s.send(data)
response = self.s.recv(8)
print("response: ")
print(response)
r_cmd = bytes.hex(response[2:3])
r_returnCode = bytes.hex(response[3:4])
if bytes.hex(response[4:8]) == "\x00\x00\x00\x00":
r_length = 0
response_payload = ""
else:
r_length = int(bytes.hex(response[4:8]), 16)
response_payload = self.read_bytes(r_length)
print("command is: %s, get return code: %s, return length: %s, \nreturn string:\n%s" % (
r_cmd, r_returnCode, r_length, response_payload))
final_response = {
"response_command": r_cmd,
"response_return_code": r_returnCode,
"response_payload_length": r_length,
"response_payload": response_payload
}
return final_response
if __name__ == "__main__":
ss = PTC()
print(ss.sender('05', None)) # Example command to 'Get Current Fault Log', change the command code and payload as needed
# save it as a CSV file
response = ss.sender('05', None)
correction_data = response.get("response_payload", b"")
with open("angle_correction.csv", "wb") as f:
f.write(correction_data)
print("The data has been saved as angle_correction.csv.")
ss.closeSocket()
- Configure the necessary Python environment in the host computer. Locate to lines 5 and 6 in the above script:
default_host = "192.168.1.201" and default_port = 9347 → Replace "192.168.1.201" and 9347 with the actual IP address and port number of the Lidar, then run the script.
After successful execution, an angle correction file named angle_correction.csv will be generated in the current directory.
3.2.1.2 DAT Format
Reference Model: AT128P
- After connecting the Lidar to the host, open the script below using an IDE:
from socket import *
sock = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
message = bytearray()
message1 = bytearray()
SN = bytearray()
# header
message.append(0x47)
message.append(0x74)
# command
##################################################################
message.append(0x05) #0x05 for Get Angle Correction File
##################################################################
# return code
message.append(0x00)
# Tail
message.append(0x00)
message.append(0x00)
message.append(0x00)
message.append(0x00) #0x01 payload data length for the command
message.append(0x00) #payload data value, 0x01 means PTP STATUS
sock.connect(("192.168.1.201",9347))#the ip of device and Port you need to call(fixed)
sock.send(message)
response=sock.recv(8)
r_cmd = int.from_bytes(response[2:3], 'big')
r_returnCode = int.from_bytes(response[3:4], 'big')
r_length = int.from_bytes(response[4:8], 'big')
response_payload=b''
while len(response_payload) < r_length:
response_payload += sock.recv(r_length)
print(response_payload)
with open("corrections.dat","wb") as f:
f.write(response_payload)
f.close()
- CConfigure the necessary Python environment in the host computer. In the above script, locate to line 24:
sock.connect(("192.168.1.201",9347))→ Replace"192.168.1.201"and9347with the actual IP address and port number of the Lidar, then run the code.
After successful execution, an angle correction file named corrections.dat will be generated in the current directory.
3.2.2 Serial Port Connection
Reference Model: JT16
- After completing the connection between the Lidar and the host as described in the user manual, open the script below using an IDE:
import struct
import csv
import serial
import time
from datetime import datetime
from threading import Thread, Event
def parse_angle_data(valid_data):
# Ensure valid_data length is 68 bytes
if len(valid_data) != 68:
raise ValueError("Valid data length must be 68 bytes")
# Initialize lists to store angle values
azimuth_values = []
elevation_values = []
# Parse Azimuth data (first 32 bytes)
for i in range(16):
azimuth_bytes = valid_data[i * 2:(i + 1) * 2]
azimuth_value = struct.unpack('<h', azimuth_bytes)[0] * 0.01 # Little-endian, short type, unit 0.01°
azimuth_values.append(azimuth_value)
# Parse Elevation data (next 32 bytes)
for i in range(16):
elevation_bytes = valid_data[32 + i * 2:32 + (i + 1) * 2]
elevation_value = struct.unpack('<h', elevation_bytes)[0] * 0.01 # Little-endian, short type, unit 0.01°
elevation_values.append(elevation_value)
return azimuth_values, elevation_values
def save_to_csv(elevation_values, azimuth_values, output_file):
with open(output_file, 'w', newline='') as csvfile:
fieldnames = ['Channel', 'Elevation (°)', 'Azimuth (°)']
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
writer.writeheader()
for i in range(16):
writer.writerow({
'Channel': i + 1,
'Elevation (°)': elevation_values[i],
'Azimuth (°)': azimuth_values[i]
})
def get_angle_correction(send_port: str, receive_port: str, baudrate_UART: int, baudrate_485: int):
# Command configuration
COMMAND = bytes([
0x24, 0x4C, 0x44, 0x43, 0x4D, 0x44, 0x2C, 0x03,
0x02, 0x07, 0x00, 0x95, 0xB3, 0x2C, 0x0A,
0xD3, 0x86, 0x1F, 0xA3, 0xEE, 0xFF
])
# Response pattern configuration
START_MARKER = bytes([0x24, 0x4C, 0x44, 0x41, 0x43, 0x4B,
0x2C, 0x48, 0x02, 0x07, 0x00])
DATA_START_OFFSET = 12 # Start position of valid data
DATA_LENGTH = 68 # Length of data to extract
ERROR_CODE_OFFSET = 80 # Position of error code
TOTAL_TIMEOUT = 8 # Total timeout in seconds
PRE_READ_TIME = 0.5 # Pre-read time in seconds
class AsyncReader:
def __init__(self, ser):
self.ser = ser
self.buffer = bytearray()
self.stop_event = Event()
self.thread = None
def start(self):
self.thread = Thread(target=self._read_loop)
self.thread.start()
def _read_loop(self):
while not self.stop_event.is_set():
if self.ser.in_waiting > 0:
chunk = self.ser.read(self.ser.in_waiting)
self.buffer.extend(chunk)
def stop(self):
self.stop_event.set()
if self.thread.is_alive():
self.thread.join(timeout=1)
def get_buffer(self):
return bytes(self.buffer)
try:
# Generate timestamped filenames
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S')
output_file = f"JT16_angle_correction_{timestamp}.dat"
log_file = f"JT16_angle_log_{timestamp}.txt"
csv_file = f"JT16_angle_correction_{timestamp}.csv"
# Open receiving port first
with serial.Serial(receive_port, baudrate_485, timeout=0) as ser_recv: # Non-blocking mode
reader = AsyncReader(ser_recv)
reader.start()
# Start receiving data in advance
print(f"[{timestamp}] Starting pre-reception...")
time.sleep(PRE_READ_TIME) # Pre-receive for 500ms
# Send command
with serial.Serial(send_port, baudrate_UART, timeout=1) as ser_send:
print(f"[{timestamp}] Sending command to {send_port}...")
ser_send.write(COMMAND)
ser_send.flush()
# Main processing loop
start_time = time.time()
found = False
with open(log_file, 'w') as log:
log.write(f"Angle Correction Process Log - {timestamp}\n")
log.write("=" * 50 + "\n")
while (time.time() - start_time) < TOTAL_TIMEOUT:
# Get current buffer
current_buffer = reader.get_buffer()
# Find start marker
pos = current_buffer.find(START_MARKER)
if pos != -1:
# Calculate required end position
required_end = pos + DATA_START_OFFSET + DATA_LENGTH + 1
if len(current_buffer) >= required_end:
# Extract response segment
response = current_buffer[pos:required_end]
# Verify data integrity
if (response[11] == 0x44 and
response[ERROR_CODE_OFFSET] == 0x00):
# Extract valid data
valid_data = response[DATA_START_OFFSET:DATA_START_OFFSET + DATA_LENGTH]
# Save as DAT file
with open(output_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(valid_data)
# # Parse angle data
# azimuth_values, elevation_values = parse_angle_data(valid_data)
#
# # Save as CSV file
# save_to_csv(elevation_values, azimuth_values, csv_file)
log.write(f"Data saved to {output_file}\n")
print(f"Correction file saved successfully: {output_file}")
print(f"CSV file saved successfully: {csv_file}")
found = True
break
# Clean up processed buffer
reader.buffer = reader.buffer[required_end:]
time.sleep(0.01) # Reduce CPU usage
reader.stop()
if not found:
error_msg = "No valid response received" if len(current_buffer) == 0 \
else f"Received {len(current_buffer)} bytes but no valid data found"
log.write(f"Error: {error_msg}\n")
raise TimeoutError(error_msg)
except Exception as e:
error_msg = f"{type(e).__name__}: {str(e)}"
print(f"An error occurred: {error_msg}")
with open(log_file, 'a') as log:
log.write(f"Error: {error_msg}\n")
raise
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Enter UART port, RS485 port, UART baud rate, RS485 baud rate respectively
# Example: Windows: COM*; Ubuntu: /dev/ttyUSB*
get_angle_correction("COM4", "COM5", 9600, 3000000)
-
Configure the necessary Python environment in the host computer, and modify the RS485 and RS232 port numbers and baud rates in the last line of the script. Note that the device names for the same serial port differ between Windows and Ubuntu systems (e.g., COM* for Windows, /dev/ttyUSB* for Ubuntu).
-
Run the script to generate an angle correction file named
JT16_angle_correction_<current_time>.datand a corresponding log file in the current directory.
Find it useful?